"The first casualty, when war comes, is truth."---Senator Hiram Johnson, 1917

My father fought in the Pacific Theatre of World War II as an Army sergeant in the Philippines, and then beyond. He was not far from Japan when the atomic bombs were dropped, and right after the peace treaty was signed, he was stationed in Japan itself for a brief period. He never spoke about it, never volunteered information, but if pressed he would tell me some thing fairly innocuous, like how a Zero suddenly appeared above their camp and sent everyone flying for cover, including the driver of a jeep, whose sudden abandonment of the vehicle sent it careening over him. Thereafter he always carried a scar on his shin from where the tires ran over his leg, and the scar, like the jungle rot in his feet that never quite went away, or his revulsion toward seafood, which had come from a steady diet of fish heads and rice, remained a constant reminder of where he'd been and what he'd done. But when he and his friends got together, or the other veterans in my family, none of them ever exchanged war stories. None of them could even be coaxed into talking about it.
He had been back from the war for almost 8 years by the time I came along. I was still a very young child when I first remember poring over the old photos he brought back, of himself and his friends posing in front of some monument with a nameless Japanese woman who smiled pleasantly for the camera. I remember thinking, even as a child, how unlikely that smile seemed. I remember running my hands over the hilt of the samurai sword he brought back as a souvenir, fascinated by that tangible link to an impossibly alien place, and how, despite all entreaties, he refused to tell me how he'd come by it. He once showed me the helmet he wore in the jungle, with the bullet hole through the gap above the webbing that had held the helmet away from his head, and I thought more than once on how close he had been to never coming home.

The popular take on those days, the post-war 50's and the early 60's, is that they were ones of halcyon innocence and peace, and endless prosperity and opportunity, and in many ways, for many people, they were. But they were also days of incredible paranoia, of enemies under every rock, and if it wasn't the Communists it was the fallout in the icicles dangling from your house, or the
Conelrad alerts and Civil Defense drills. My uncle, a classic sailor with fascinating tattoos on his muscular forearms, had by then become a career Navy man, and went from World War II to Korea hardly missing a beat, while
Joe McCarthy was hard at work creating the seige mentality that would enable our governments to justify sending us to war for decades to come. By then the phrase used so hopefully during the First World War, that "war to end all wars", was beginning to look a little threadbare. Still, after being fed a steady diet of
nationalist propaganda,
cover-ups, and
re-written history, we were psyched to shrug our collective shoulders with a sigh, accept that this was just the way it would have to be, and ready to embark on the brave new world of
industrial slaughter those in power
had in mind for us.
Never have a nation's demurs against war rung so blatantly false or
for so long. Even now we delude ourselves into thinking that we are never aggressive, never looking for a fight,
always being pushed into situations where war is our only option and therefore justified.

Here we are, always just minding our own business, and along comes some pushy country just spoiling for a fight. The fact that for the last 60 years those
pushy countries have happened to be
small,
powerless, backward,
irrelevant, or all four, has somehow failed to make an impression on a people whose national myth includes standing up for the underdog and playing the part of the hero. That was the story we told ourselves in World War II, and that is the story we continue to tell throughout the subsequent years of evidence to the contrary.
It was in 1975 that in "Home to Roost", her speech on the state of the union immediately after Watergate,
Hannah Arendt lamented the desperate lengths to which we went to make ourselves feel good after the humiliation of Vietnam:
"What comes home to roost now is this long education in imagery (i.e., the retreat from uncomfortable truths and quest for lies from which to create positive images), which seems no less habit-forming than drugs. Nothing in my opinion told us more about this addiction than the public reaction, on the street as well as in Congress, to our 'victory' in Cambodia, in the opinion of many 'just what the doctor ordered' (Sulzberger) to heal the wounds of the Vietnam defeat. Indeed, 'Twas a famous victory!' as James Reston aptly quoted in the New York Times, and let us hope that this was finally the nadir of the erosion of self-confidence when victory over one of the tiniest and most helpless countries could cheer the inhabitants of what only a few decades ago really was the 'mightiest power on earth."

So the anniversary of the use of the atomic bomb against human beings is being noted this weekend, and as it inevitably will, the
discussion has arisen as to whether it was justified. The
usual arguments are made for it: that a million servicemen's lives were saved, that Japan would have never surrendered otherwise, that an example had to be made to ensure their will was broken and they never became a threat again, that Truman warned them and they wouldn't listen. That something good came out of it after all. That like the war itself, it was a moral action justified in the cause of eradicating evil. That it was a lesser evil chosen for a greater good.
My head, much like Hiroshima, wants to explode.
There are plenty of sites on the internet and at the library where you can immerse yourself in the facts and fantasies that surrounded the event, and although I believe the bombings were the greatest atrocities my nation ever committed (and I do not believe they saved my father's life), I'm more interested in the idea of a "moral" war.
Chris Hedges, in his wonderful book,
Losing Moses on the Freeway, calls on his many years as a war reporter, and interview with a Vietnam vet who went on to become a Bishop in the Episcopal church, to answer those who posit the existence of a moral war. After recounting incidents from the war in which the bishop committed acts he would have never thought himself capable, Hedges says this:
"Bishop Packard discovered in the war the capacity we all have for evil. He discovered the darkness that allows us, when the restraints are cut, to commit acts of brutality against the weak and the defenseless, including children. He discovered the ghoulish delight soldiers can take in killing"
And to answer the suggestion that war can be moral, he says this:
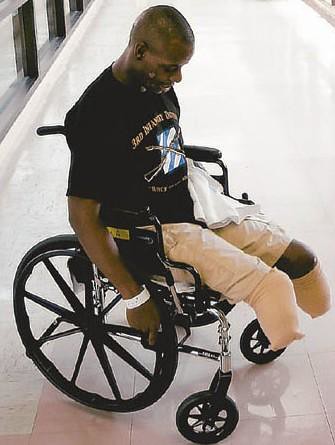 "Wars come wrapped in patriotic slogans, call for self-sacrifice and glory. They come wrapped in the claims of divine providence... It is what is right and just. War is always waged...to make the nation and the world a better place, to cleanse evil...
"Wars come wrapped in patriotic slogans, call for self-sacrifice and glory. They come wrapped in the claims of divine providence... It is what is right and just. War is always waged...to make the nation and the world a better place, to cleanse evil...
But up close war is a soulless void. War quickly descends to raw barbarity, perversion, pain and an unchecked orgy of death. It is a state where human decency and tenderness are crushed, where those who make war work overtime to destroy love, where all human beings become objects to use or kill. The noise, the stench, the fear, the eviscerated bodies and bloated corpses, the crying wounded spin us into another universe. In this moral void, blessed by institutions at home, the hypocrisy of our social conventions are laid bare. We call for strict adherence to some commandments and laud the purposeful violation of others. Hypocrisy rules. War, for all its horror, has the power to strip away the trivial and the banal, the empty chatter and foolish obsessions. It lets us see."
War is evil. It is the industrial slaughter of human beings we do not know, and when our weapons hit their marks, we can't possibly know whether one of them lays low a deserving victim or not. We cannot help but
kill non-combatants, many of whom are children, old people, pregnant women, mothers, fathers, sisters, people who were loved as much as we ourselves are loved, and whose claim to the right to life is as strong and legitimate as any of our own. When we engage in it, for whatever reason, we do evil, and commit sin.

Yet, with few
exceptions, you seldom hear the institutionalized religions speak out against government when war is waged. How often did you hear the voices of the churches of the land raised in protest and condemnation as Bush pushed the country inexorably toward Iraq? How often do your hear churches, so eager to
shut off communion for politicians in favor of choice, threaten the same for those who support and fight the war? The most
self-righteous and judgmental of them actually
praise it as a
just retribution, and
support those who engineered and maintain it. Their religion is actually a civic one, and as Hedges states:
"These institutions have little or nothing to say in wartime because the god they worship is often a false god, one that promises victory to those who obey the law and believe in the manifest destiny of the nation. The god of war takes over the pulpits and airwaves. Religious leaders line up to bless the enterprise of war."
When religion and the state become one, they enable one another, and the combined force of their authority can push a nation into committing
any conceivable horror.
Robert Jay Lifton told Hedges:

""Ordinary men can all too readily be socialized to atrocity. These killing projects are never described as such. They are put in terms of the necessity of improving the world, of political and spiritual renewal. You cannot kill large numbers of people without a claim to virtue. Our own campaign to rid the world of terror is expressed this way, as if once we destroy all terrorists we destroy evil."
This is the lesson of Abu Ghraib, and Guantanamo, and Bagram: when we choose torture because we are "forced to by desperate circumstances", when we drop a nuclear bomb because we must "eliminate the danger posed by Japan for all time", we bargain with demons. The bargain says:
"We know we do evil but it's a lesser evil, and we hope we won't have to do this again, but if we do, we hope you forget that we promised you our soul". Hannah Arendt said this about lesser evils:
"Politically, the weakness of the argument has always been that those who choose the lesser evil forget very quickly that they choose evil... Acceptance of lesser evils is consciously used in conditioning the government officials and the population at large to the acceptance of evil as such."
We have already chosen far too much of the lesser evil, and have been doing so for decades. How much more can we choose before it becomes indistinguishable from the very evil we thought we were running away from?



 This is where about 8,000+ of New Orleans' poorest residents have taken shelter, in the Superdome. The NYTimes reports now even that imposing structure is taking
This is where about 8,000+ of New Orleans' poorest residents have taken shelter, in the Superdome. The NYTimes reports now even that imposing structure is taking 







 According to the most recent on-line edition of
According to the most recent on-line edition of 

 While America shops, Iraq continues to crumble into a
While America shops, Iraq continues to crumble into a 



 Cindy Sheehan has asked that those who support her cause start candlelight vigils in their own communities across the country. Tonight is your chance to stand up and be counted. Helping coordinate this event (as if you couldn't tell from the graphic) are
Cindy Sheehan has asked that those who support her cause start candlelight vigils in their own communities across the country. Tonight is your chance to stand up and be counted. Helping coordinate this event (as if you couldn't tell from the graphic) are  If you can't wait that long, but would be happy with a fake president who was at least amusing, you could try
If you can't wait that long, but would be happy with a fake president who was at least amusing, you could try 


 What's the matter with Kansas?
What's the matter with Kansas?  My father fought in the Pacific Theatre of World War II as an Army sergeant in the Philippines, and then beyond. He was not far from Japan when the atomic bombs were dropped, and right after the peace treaty was signed, he was stationed in Japan itself for a brief period. He never spoke about it, never volunteered information, but if pressed he would tell me some thing fairly innocuous, like how a Zero suddenly appeared above their camp and sent everyone flying for cover, including the driver of a jeep, whose sudden abandonment of the vehicle sent it careening over him. Thereafter he always carried a scar on his shin from where the tires ran over his leg, and the scar, like the jungle rot in his feet that never quite went away, or his revulsion toward seafood, which had come from a steady diet of fish heads and rice, remained a constant reminder of where he'd been and what he'd done. But when he and his friends got together, or the other veterans in my family, none of them ever exchanged war stories. None of them could even be coaxed into talking about it.
My father fought in the Pacific Theatre of World War II as an Army sergeant in the Philippines, and then beyond. He was not far from Japan when the atomic bombs were dropped, and right after the peace treaty was signed, he was stationed in Japan itself for a brief period. He never spoke about it, never volunteered information, but if pressed he would tell me some thing fairly innocuous, like how a Zero suddenly appeared above their camp and sent everyone flying for cover, including the driver of a jeep, whose sudden abandonment of the vehicle sent it careening over him. Thereafter he always carried a scar on his shin from where the tires ran over his leg, and the scar, like the jungle rot in his feet that never quite went away, or his revulsion toward seafood, which had come from a steady diet of fish heads and rice, remained a constant reminder of where he'd been and what he'd done. But when he and his friends got together, or the other veterans in my family, none of them ever exchanged war stories. None of them could even be coaxed into talking about it. The popular take on those days, the post-war 50's and the early 60's, is that they were ones of halcyon innocence and peace, and endless prosperity and opportunity, and in many ways, for many people, they were. But they were also days of incredible paranoia, of enemies under every rock, and if it wasn't the Communists it was the fallout in the icicles dangling from your house, or the
The popular take on those days, the post-war 50's and the early 60's, is that they were ones of halcyon innocence and peace, and endless prosperity and opportunity, and in many ways, for many people, they were. But they were also days of incredible paranoia, of enemies under every rock, and if it wasn't the Communists it was the fallout in the icicles dangling from your house, or the  Here we are, always just minding our own business, and along comes some pushy country just spoiling for a fight. The fact that for the last 60 years those
Here we are, always just minding our own business, and along comes some pushy country just spoiling for a fight. The fact that for the last 60 years those  So the anniversary of the use of the atomic bomb against human beings is being noted this weekend, and as it inevitably will, the
So the anniversary of the use of the atomic bomb against human beings is being noted this weekend, and as it inevitably will, the  "Wars come wrapped in patriotic slogans, call for self-sacrifice and glory. They come wrapped in the claims of divine providence... It is what is right and just. War is always waged...to make the nation and the world a better place, to cleanse evil...
"Wars come wrapped in patriotic slogans, call for self-sacrifice and glory. They come wrapped in the claims of divine providence... It is what is right and just. War is always waged...to make the nation and the world a better place, to cleanse evil... Yet, with few
Yet, with few 



